Superfetch is a Windows process that runs in the background of your computer system. Earlier it was known by other names like ‘Prefetch’ on Windows XP. It was introduced on Windows Vista, and since then, the term has been changed based on its working process.
If you are a Windows 10 OS user, then you can identify it as Sysmain in your system. The intendment of every generation of the Superfetch process has always been the same; it helps Windows increase its performance by preloading the frequently used applications into the RAM before you need to enforce them.
You can see it on the Task Manager as ‘Sysmain’ on the latest version of Windows. If you are using an older version of Windows 10 or Windows 7/8, you can check it as Service Host: Superfetch in the Task Manager.
What is Superfetch?
Superfetch is a feature introduced by Microsoft in Windows Vista operating system. As per the official description, it works to maintain and improve the performance of the system. However, the said statement doesn’t justify its purpose to the extent.
Superfetch runs in the background to analyze the RAM usage patterns. It examines what applications are being used regularly by the user. Mostly, Superfetch is quite useful if you have a modern PC with an average directive. It runs so swimmingly that the user won’t even know. It will of your Windows 10.
Is it right to Disable Superfetch?
As stated earlier, the Superfetch process runs in the computer background to preload frequently used apps into the RAM ahead of the time for the user’s convenience. As far as the PC’s safety is concerned, there is nothing harmful in the said process.
However, sometimes some issues can occur with Superfetch being active on your system. Superfetch is always running in the background, and occasionally it can use a considerable amount of CPU and RAM storage that might slow down the system. It doesn’t stamp out the process of loading apps into RAM. It relocates the loading ahead of time, and that’s why the PC still goes through the slow loading experience as before.
If your Windows 10 is installed on an SSD, you don’t even need Superfetch considering how fast the SSDs are, and they don’t need preloading to run an application. It has also been known to cause issues while playing games on computers with 4GB or less RAM.
How to Disable Superfetch in Windows 10?
If you have been facing any of the above issues, or if you think you don’t need Superfetch in your computer to preload the frequently used applications, you can always opt for disabling it from your computer system.
Please follow the below steps to disable Superfetch on your PC.
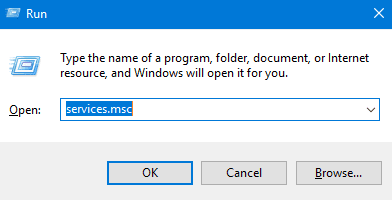
Step 1. Open the Service app by typing ‘services’ in the search bar or alternately press Window + R keys simultaneously to open the Run prompt and type ‘services. MSC‘ and click Ok to launch the Services app.
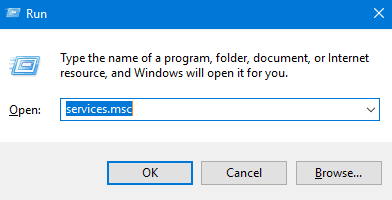
Step 2. Once the ‘Services‘ page opens, scroll down and locate ‘Superfetch,’ then right-click on it and click on the ‘Stop’ option to disable it.
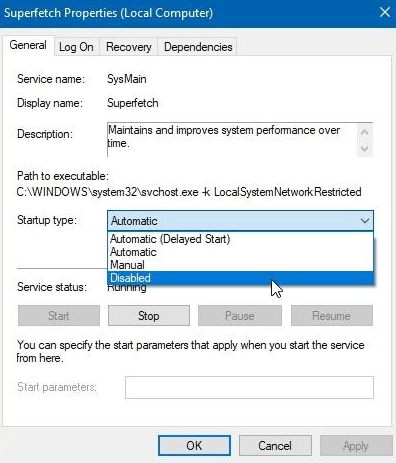
Step 3. Forestall the said process to enable automatically, right-click on ‘Superfetch’ in the Service app and select the ‘Properties’ option under the ‘General’ tab.
Step 4. Navigate to the ‘Startup type‘ section, and select ‘Disabled.’ If you want to use it in the future, select the ‘Manual’ option.
Final Words
Superfetch has been known to ease up the loading process for the applications you regularly use on your computer. The said process is quite useful for enhancing the performance of your computer. However, sometimes it can create some issues using a vast amount of RAM and causing a poor user experience, especially while playing games on the computer.
Keeping Superfetch in your system is no harm, but if you face any performance-related problems, you can always opt for disabling it.
Please go through all the details mentioned earlier and the steps before disabling your PC’s said service.
We hope that we have guided you profoundly to clear the essential aspects of Superfetch. Thank you for reading our article.